
The New Rental Laws 2025 aim to provide comprehensive protections for tenants across India, curbing arbitrary rent hikes and unlawful evictions. The legislation standardizes rental agreements, introduces deposit limits, and enforces a structured eviction process, according to the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA). Experts view the reforms as a critical step toward formalizing the rental housing sector.
Historical Context of Rental Laws in India
India’s rental sector has long been characterized by informal agreements and uneven legal protections. Pre-2025 tenancy laws were fragmented across states, often allowing landlords significant discretion over rent increases and evictions. Many tenants in metropolitan cities such as Delhi, Mumbai, and Bengaluru faced sudden displacement due to unregulated rent hikes.
Rent control acts implemented decades ago often froze rents at levels significantly below market rates, disincentivizing landlords from maintaining properties. Over time, this contributed to housing shortages, a proliferation of informal agreements, and disputes between landlords and tenants.
Key Provisions of the New Rental Laws 2025
Mandatory Written and Registered Agreements
The legislation requires all residential rental agreements to be in writing and digitally registered. Oral agreements are no longer legally sufficient. Registered leases must clearly define the rent, security deposit, duration, and notice periods.
Dr. Anya Sharma, senior fellow at the Brookings Institution, stated, “Digital registration ensures transparency and reduces informal tenancy disputes, providing legal clarity for both landlords and tenants.”
Security Deposit Caps
The laws cap residential security deposits at two months’ rent. Landlords retaining deposits beyond this limit may face legal action. The regulation aims to reduce the upfront financial burden for tenants, particularly for students, young professionals, and migrant workers in high-demand urban centers.
Controlling Rent Hikes
Sudden rent hikes are prohibited. Landlords can only increase rent according to terms in the registered lease, with a minimum three-month notice. Experts note that this measure stabilizes rental affordability while maintaining a fair return for landlords.
Housing and Urban Development Research Institute (HUDRI) reports predict that these controls could prevent displacement of low- and middle-income households in urban areas.
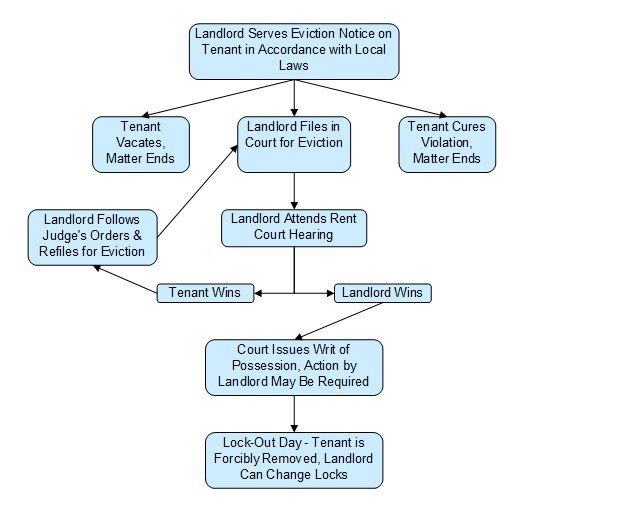
Eviction Protections
Evictions require defined grounds such as non-payment of rent, property damage, or the landlord’s genuine personal need. Arbitrary or retaliatory evictions are prohibited. Tenants can challenge eviction notices through state rent authorities or courts, ensuring due process.
Priya Kapoor, housing law expert, explained, “The legislation enforces a structured process, preventing sudden displacement while allowing landlords to reclaim property under legitimate conditions.”
Comparative International Perspective
India’s reforms align with global trends in tenant protection. Countries like Germany and the UK regulate rent increases, enforce long-term lease stability, and require proper notice for eviction. In the United States, rent control varies by state and city, but tenant protection laws often provide a formal grievance mechanism similar to India’s new rent authorities.
This international comparison highlights India’s efforts to modernize tenancy regulation while balancing landlord and tenant rights.
Stakeholder Impact
Tenants
The laws reduce uncertainty, ensuring housing stability and protection from exploitative practices. They also clarify rights regarding security deposits and maintenance responsibilities.
Landlords
While some landlords may perceive restrictions on rent hikes as limiting profitability, experts argue that formalized agreements reduce disputes and enhance long-term rental yield security.
Real Estate Market
Formalization of rental agreements may increase investor confidence and promote professional property management, particularly in metropolitan areas experiencing high demand for rental housing.
Implementation and State Variation
States have flexibility in adapting the laws to local conditions. Some have launched online portals for registration, complaint resolution, and monitoring rent hikes. Tenants and landlords are encouraged to consult state-specific regulations to ensure compliance.
Practical Guidance for Tenants and Landlords
- Register agreements digitally where mandated.
- Document property condition at move-in and move-out to avoid deposit disputes.
- Track lease terms for permitted rent hikes and renewal clauses.
- Dispute resolution can be sought through state rent authorities or courts.
These steps ensure compliance and reduce conflicts under the new legal framework.
Haryana Government Releases New Guidelines for Financial Aid to Families of Freedom Fighters
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite comprehensive provisions, challenges persist. Enforcement in rural areas and smaller towns may be limited due to lack of awareness and infrastructure. Informal rentals remain prevalent. Experts recommend public awareness campaigns, capacity-building for rent authorities, and continued digital integration for monitoring and compliance.
Dr. Sharma observed, “The long-term success of the New Rental Laws 2025 will depend on effective enforcement and education for both tenants and landlords.”
FAQ About New Rental Laws 2025
Q: Can a landlord evict a tenant without reason?
A: No. Evictions require legally defined grounds under the New Rental Laws 2025.
Q: What is the maximum security deposit?
A: Two months’ rent for residential properties, unless otherwise specified by state laws.
Q: How often can rent be increased?
A: Only as agreed in the registered lease, with a minimum notice of three months.
Conclusion
The New Rental Laws 2025 signify a major milestone in India’s housing sector, enhancing tenant protections and formalizing rental agreements. By regulating rent increases, deposits, and eviction procedures, the legislation seeks to balance landlord and tenant interests while promoting housing stability and transparency.
















